Retinotopic Foveated Rendering
Yan Zhang1, Keyao You1, Xiaodan Hu2, Hangyu Zhou1, Kiyoshi Kiyokawa2, and Xubo Yang1†
1: Shanghai Jiao Tong University
2: Nara Institute of Science and Technology
†: Corresponding author
Abstract
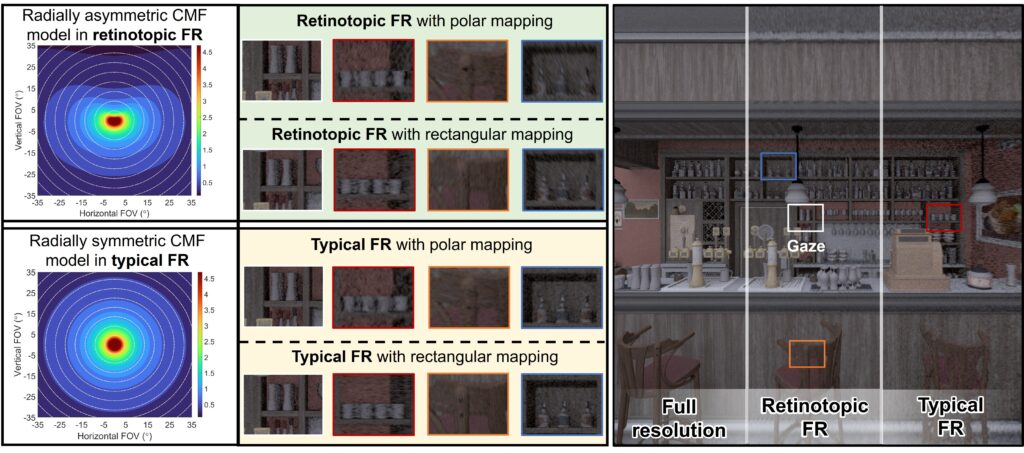
Foveated rendering (FR) improves the rendering performance of virtual reality (VR) by allocating fewer computational loads in the peripheral field of view (FOV). Existing FR techniques are built based on the radially symmetric regression model of human visual acuity. However, horizontal-vertical asymmetry (HVA) and vertical meridian asymmetry (VMA) in the cortical magnification factor (CMF) of the human visual system have been evidenced by retinotopy research of neuroscience, suggesting the radially asymmetric regression of visual acuity. In this paper, we begin with functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data, construct an anisotropic CMF model of the human visual system, and then introduce the first radially asymmetric regression model of the rendering precision for FR applications. We conducted a pilot experiment to adapt the proposed model to VR head-mounted displays (HMDs). A user study demonstrates that retinotopic foveated rendering (RFR) provides participants with perceptually equal image quality compared to typical FR methods while reducing fragments shading by 27.2% averagely, leading to the acceleration of 1/6 for graphics rendering. We anticipate that our study will enhance the rendering performance of VR by bridging the gap between retinotopy research in neuroscience and computer graphics in VR.
Keywords: Virtual reality, mixed reality, foveated rendering, ray tracing, retinotopy, functional magnetic resonance imaging
Video
Citation
TBD